Symmetry in biology is the balanced distribution of duplicate body parts or shapes within the body of an organism. In nature and biology, symmetry is always approximate. Symmetry creates a class of patterns in nature, where the quasi-repetition of the pattern element is of reflection or rotation. Simmetria organismi marini Symmetry marine species
The body planes of most multicellular organisms exhibit some form of symmetry, whether radial, bilateral, or spherical. A small minority, particularly among sponges, exhibit asymmetry (i.e., they are asymmetrical).
https://it.qwe.wiki/wiki/Symmetry_in_biology
Animal symmetry is a feature common to all eumetazoi. In fact, these living beings are characterized by particular properties of symmetry that allow them to be classified into two main branches:
- the radiates, characterized by radial symmetry;
- the bilateral, characterized by a single plane of symmetry.
https://it.wikipedia.org/wiki/Simmetria_animale
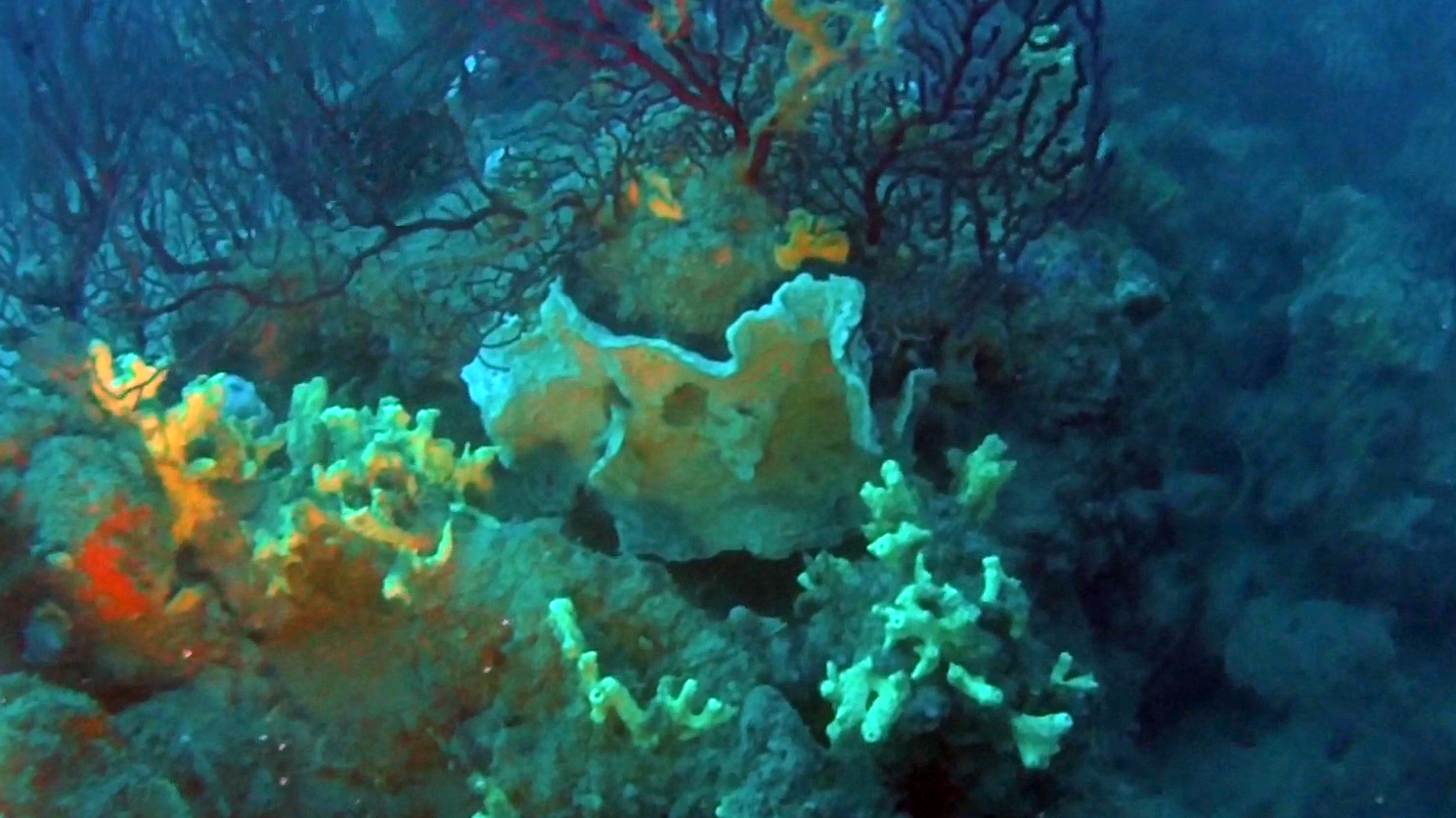
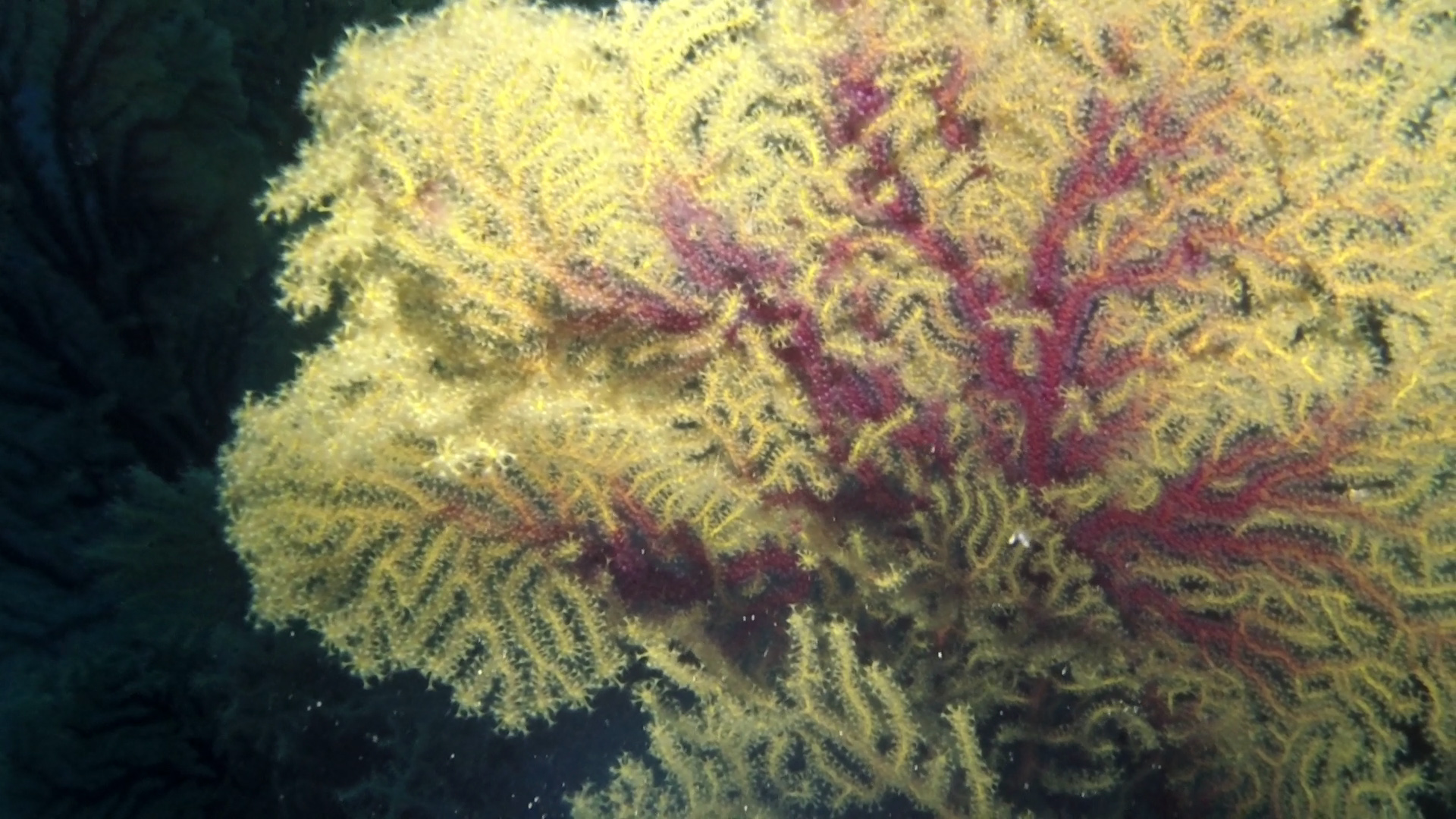
Anthozoans (Anthozoa Ehrenberg, 1831) are a class of animals (marine invertebrates) from the Cnidaria phylum. With over six thousand species, both solitary and colonial, it is the largest taxon of the Cnidaria.
They consist of small single polyps or typically clustered in colonies of many similar individuals. The group includes organisms commonly known as corals, builders of tropical coral reefs, which, by producing calcium carbonate in the form of calcite, form the typical limestone skeleton.
They also include sea anemones (anemonia), pinnatulae, soft corals.
The corals all belong to the Anthozoa class and are divided into three monophyletic subclasses (Octocorallia, Hexacorallia and Ceriantharia) depending on the number of tentacles, the line of symmetry, their exoskeleton, the type of nematocysts or the genetic analysis. Corals with eight tentacles are called Octocorallia (or Alcyonaria), those with more than eight tentacles in multiples of six are called Hexacorallia (in the past also called Zoantharia, a denomination now limited to an order).

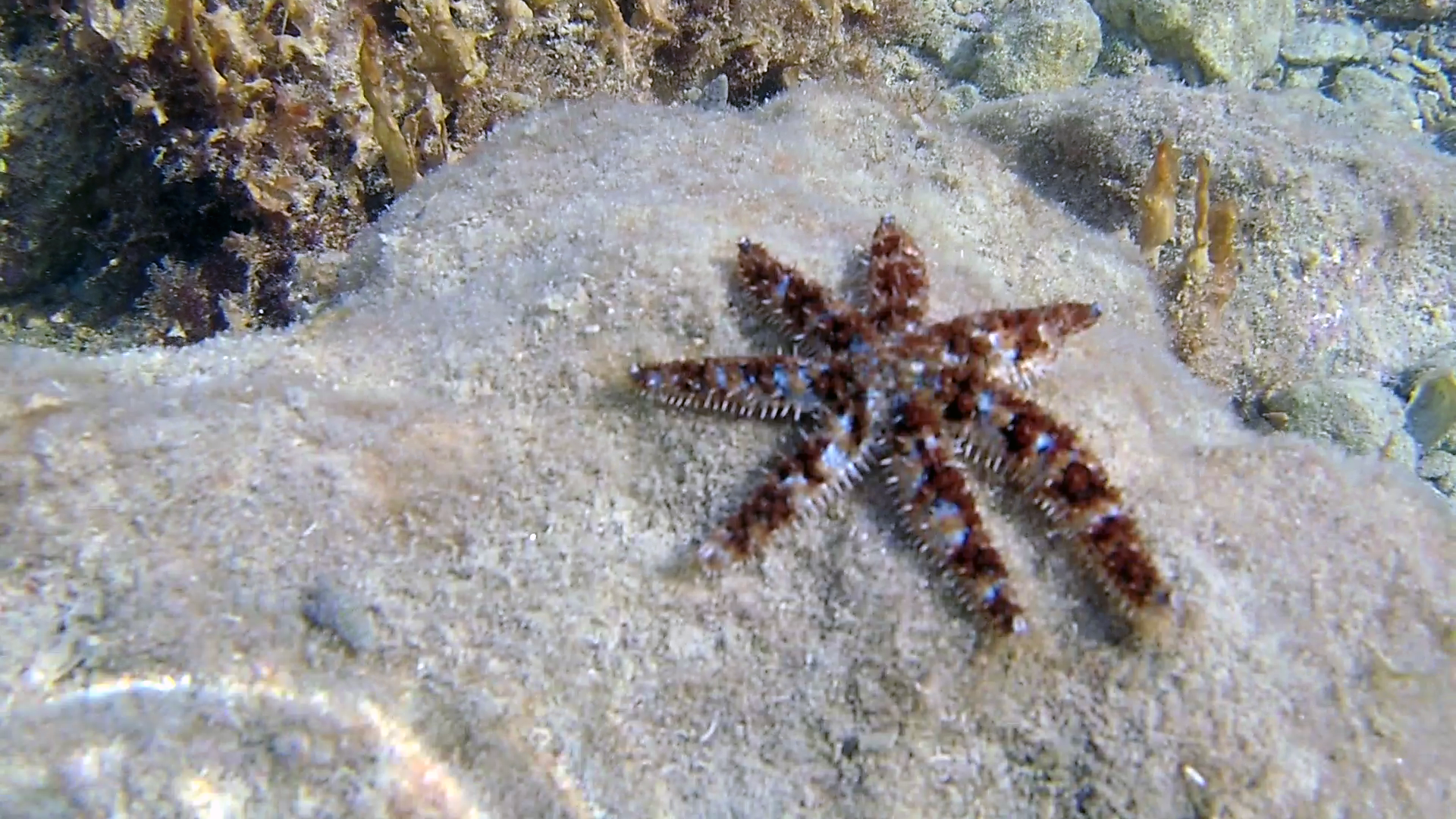
Stella marina variabile (lato inferiore) – the blue spiny starfish (underside) – Coscinasterias tenuispina – intotheblue.it
The Variable Star belongs to the philum of the Echinoderms and to the class of Asteroids.
Echinoderms are benthic organisms characterized by the presence of a calcareous “skeleton” formed by plates, welded or articulated, placed under the epidermis called dermaskeleton, often covered with tubercles or thorns, which gives the name to the philum. Another characteristic of all the organisms of the philum is the so-called pentameral symmetry; that is, the body is divided into five sectors arranged around a central axis. And this is perhaps the characteristic that has led scholars to include organisms with such different appearances in the same philum. We find five classes in this philum:
– crinoids
– holothurioids
– ofiuroidei
– asteroids
– echinoidei
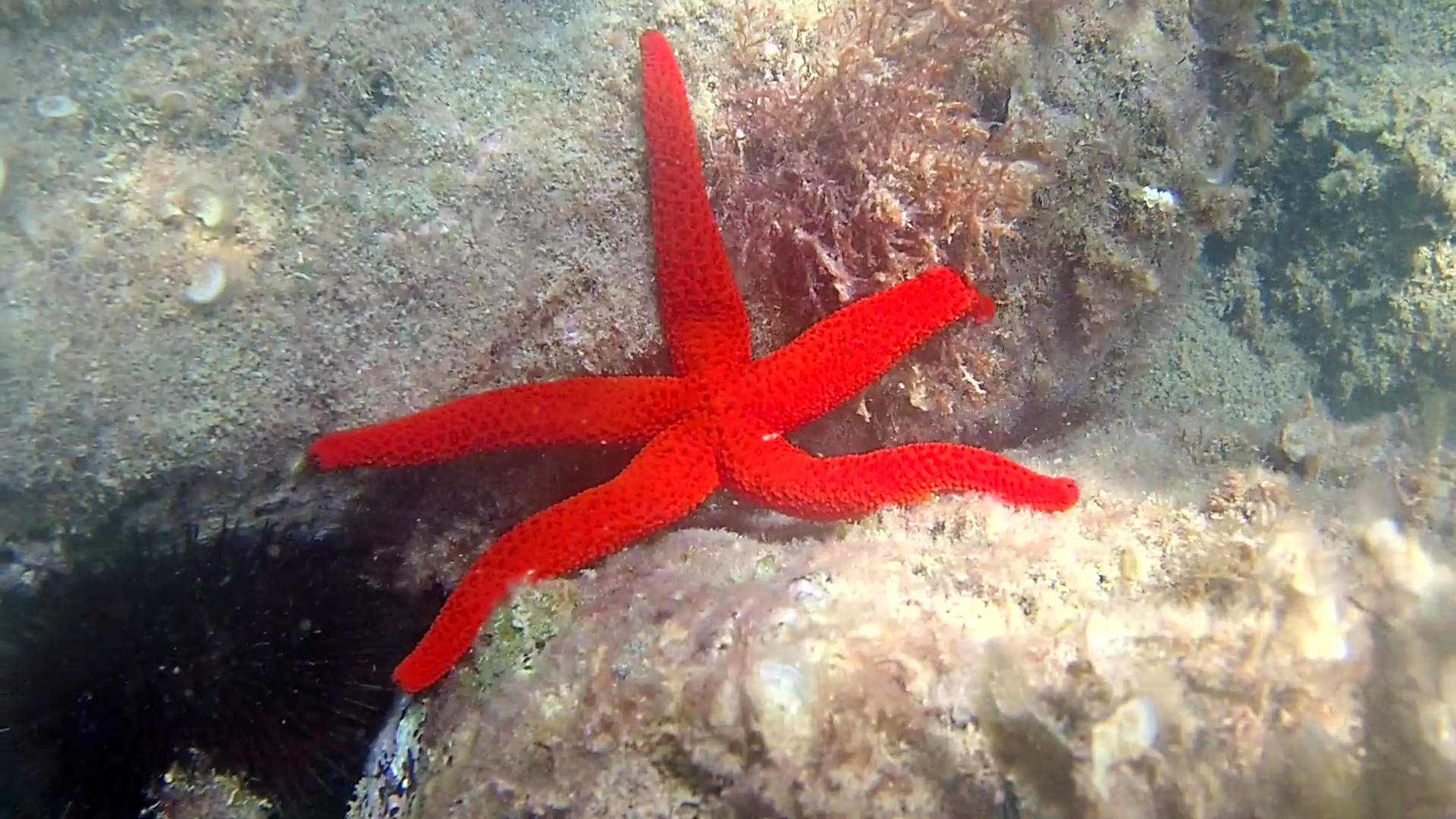
Asteroids are universally known as starfish. Starfish are flat, disc-shaped organisms protected by limestone plates hinged to the muscular system. Five or more arms branch off from the disc. A groove in the lower median part of each arm collects the pedicels suitable for walking. The regenerative capacity of the starfish arms is known.
The variable spiny star is a starfish with more than 5 arms equipped with warts and suckers also in the upper part.
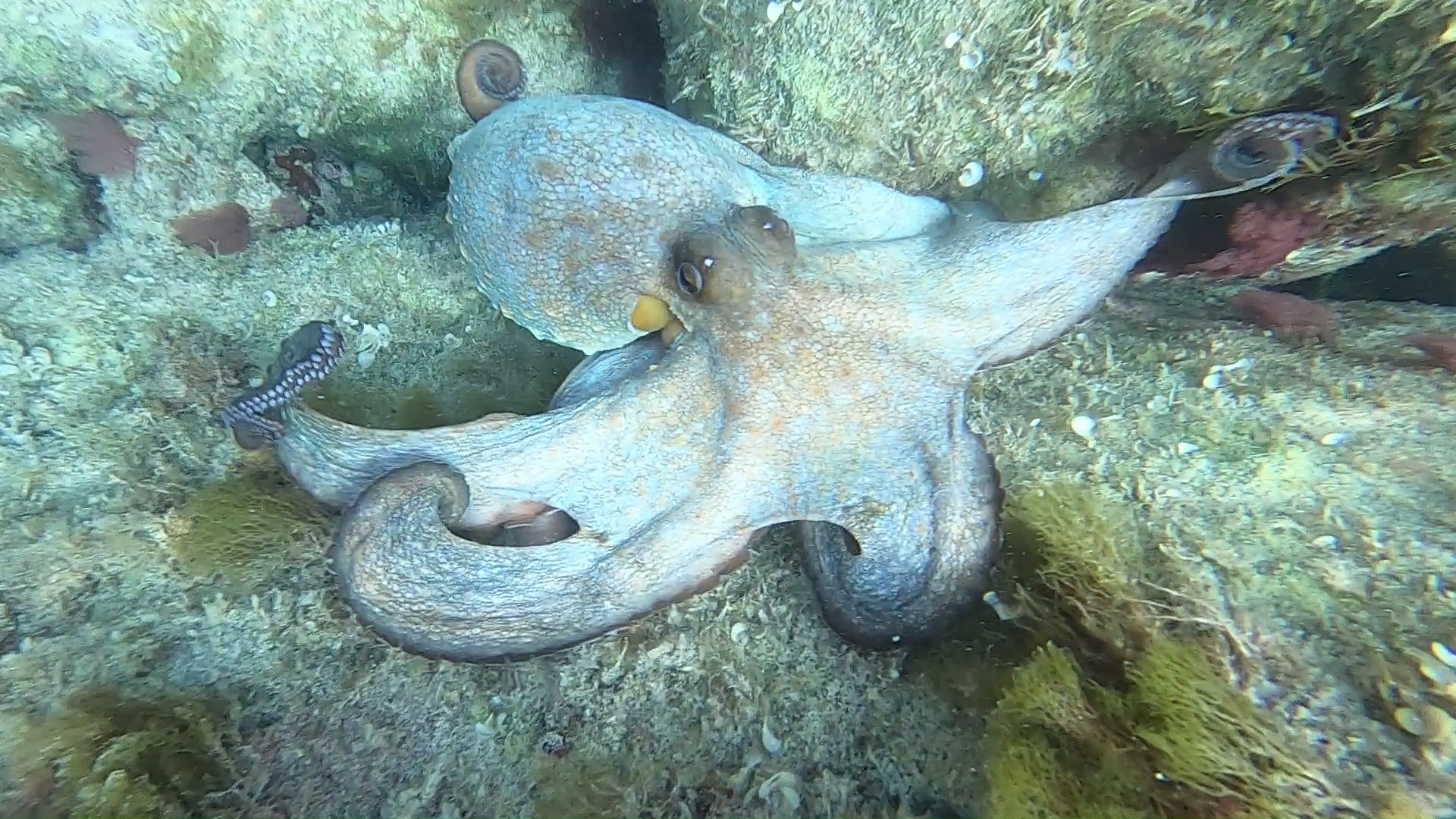
The octopus (Octopus vulgaris Cuvier, 1797) is a cephalopod of the family Octopodidae. In common use it is improperly called also polyp, but it must not be confused with the this, a name which in zoology belongs only to the fixed life stages of the coelenterate phylum, such as those of corals. https://it.wikipedia.org/wiki/Octopus_vulgaris
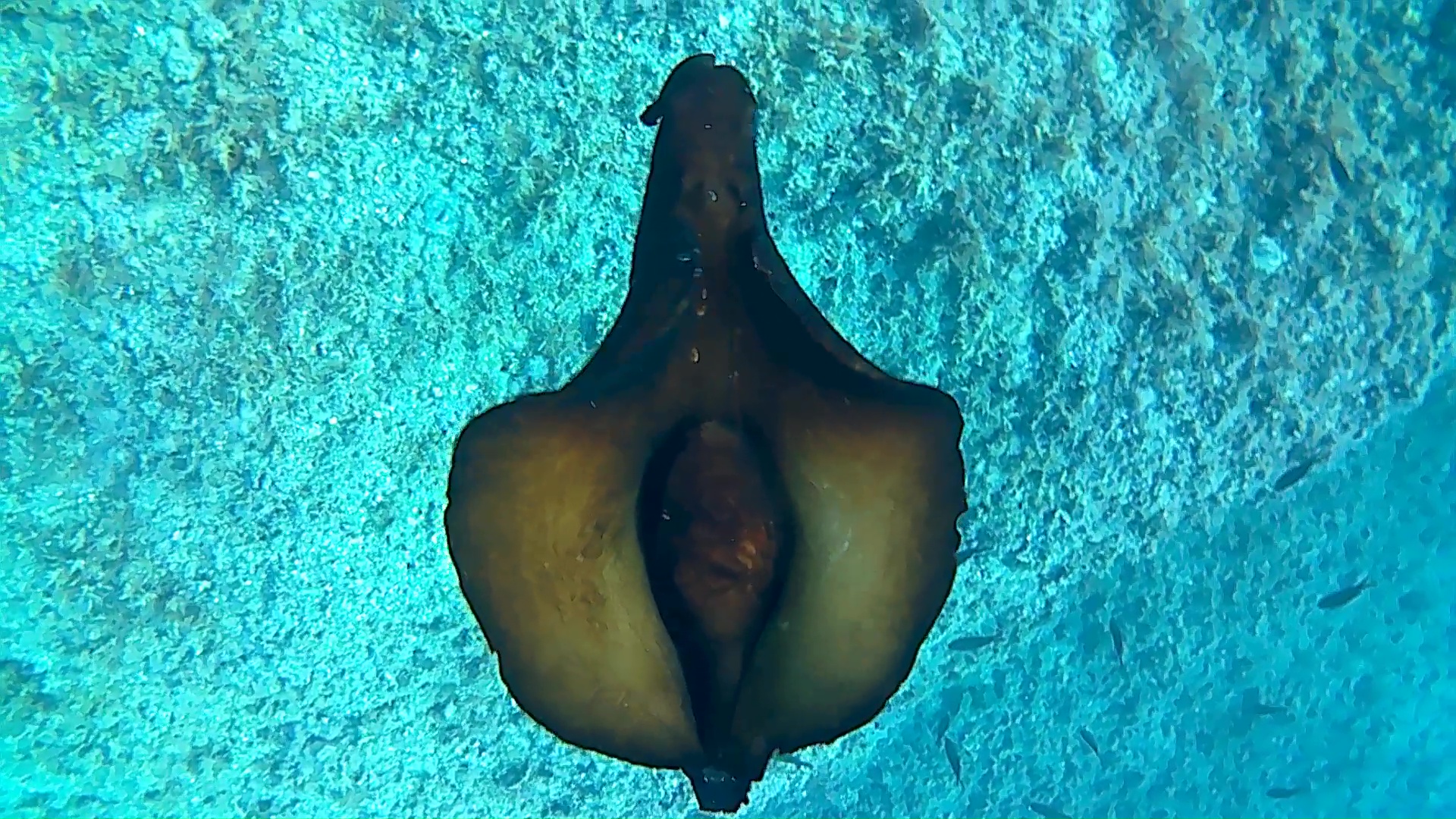
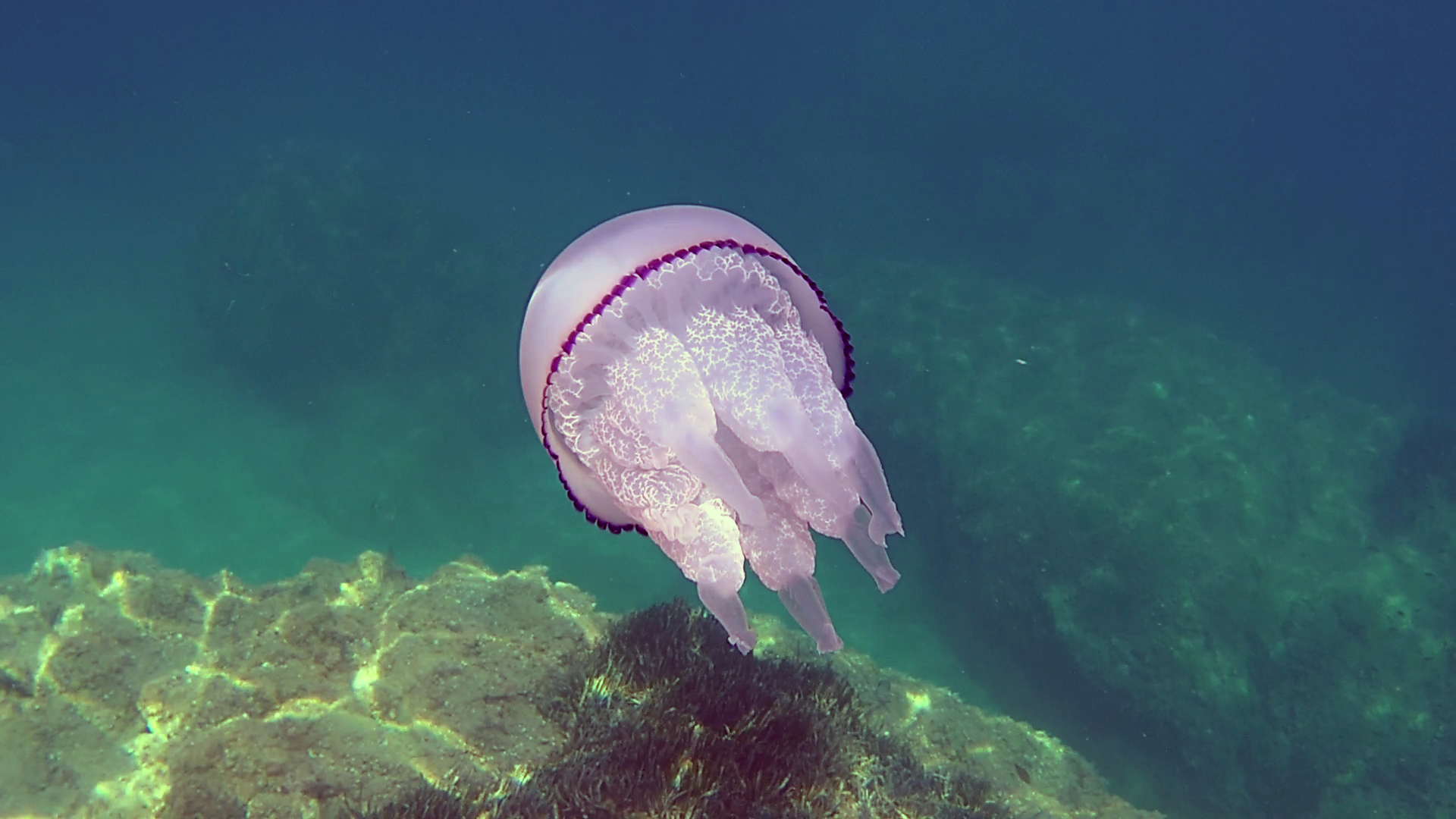
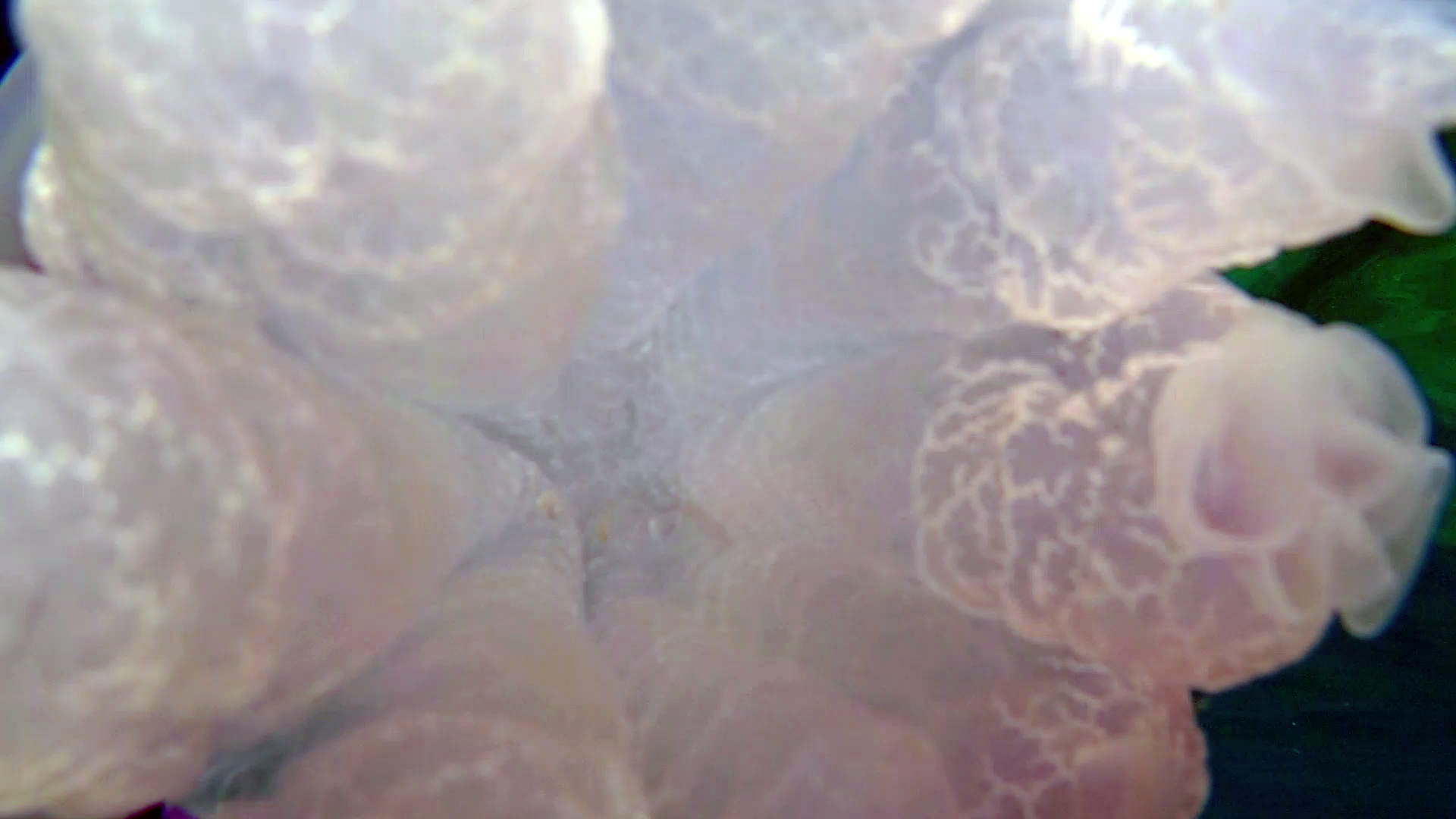
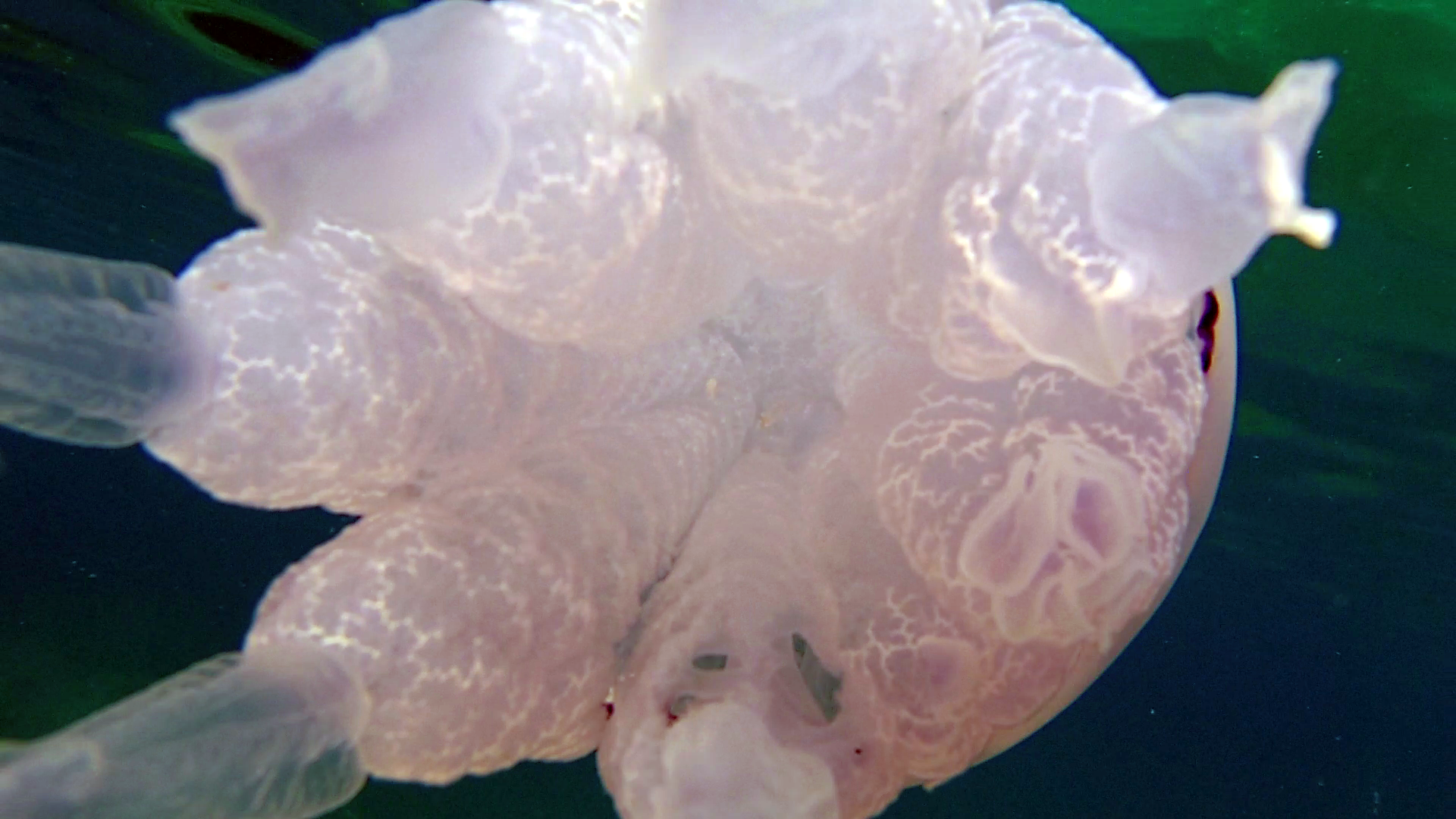
The Barrel Jellyfish or Rhizostoma Pulmo, is a scifomedusa of the Rhizostomatidae family.
This jellyfish has an opalescent but tending to transparent hemispherical hat, with blue-purple fringed edges. Under the hat, the body is called the manubrium and is composed of 8 extensions of curled and lumpy white-transparent fabric, from which 8 elongated, frayed and semi-transparent tentacles start. The young specimens tend to have a more transparent color, the adults much more opalescent. The common name of sea lung is due to the typical throbbing movement made by the jellyfish to move. The dimensions are noteworthy: being able to reach 50-60 cm in diameter and 10 kg in weight, it represents the largest jellyfish in the Mediterranean.
Scyphozoans generally have a tetraradial (or tetraradial, 2-axis) symmetry and have an internal gelatinous material called the mesoglea, which separates the ectoderm and endoderm, and which provides the jellyfish with the same structural integrity as a skeleton. The mesoglea comprises motile amoeboid cells from the epidermis. https://it.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scyphozoa
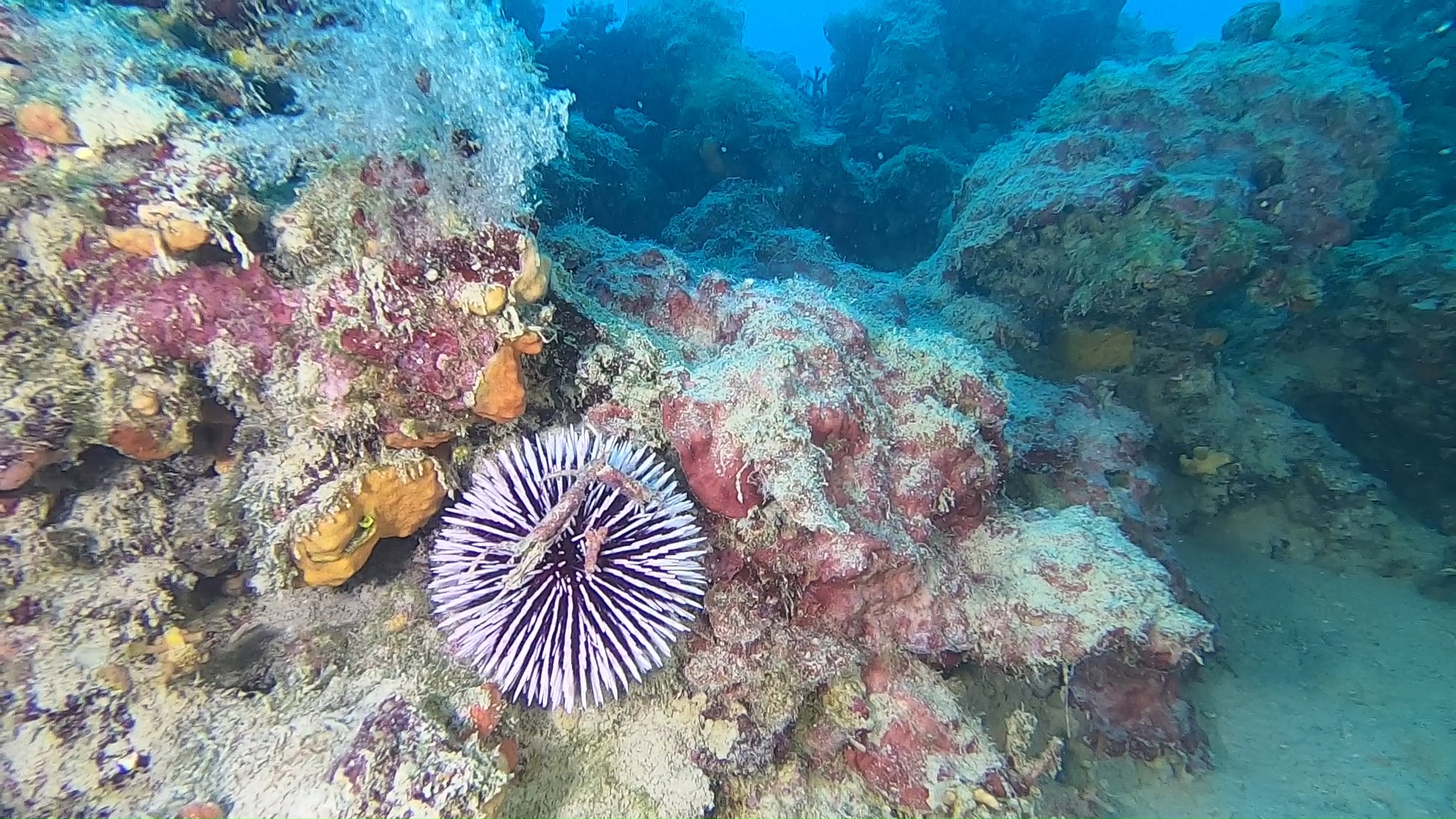
Echinoidea Leske, 1778 is a class of the phylum Echinodermata that includes marine organisms commonly referred to as sea urchins.
Many elements lead to a pentagonal symmetry (such as the five ambulatory sectors, the five radial channels, the five pyramid structure of Aristotle’s lantern), but it is actually pseudo-pentagonal, since the madreporite is unequal and allows to identify a bilateral axis of symmetry. The symmetry is instead exclusively bilateral in the Irregular Echinoids.
 English
English Italiano
Italiano